Initial Evaluation Of Woman
Women's problems are responsible for approximately 40-45% of the couples not being able to conceive. These are; Ovulation disorders, Age factor, Diminished ovarian reserve, Damaged and blocked tubes, Endometriosis, Problems related to the cervix, Uterine problems, Polycystic ovarian Syndrome (PCOS),Allergic reasons.
While investigating the causes of infertility in women the history of women is questioned by considering the following factors:
- The age of the woman.
- The infertility period and results of previous evaluations and treatments.
- Menstrual cycle pattern (regular menstruation, ovulation pain, breast tenderness, mid-menstrual spotting may suggest ovulation, while painful menstruation might suggest endometriosis).
- Medical, surgical and gynecological history (sexually transmitted disease, Pelvic inflammatory disease history, treatment of abnormal pap smear, previous abdominal surgery). At least while reviewing the systems, patients should be questioned in terms of thyroid diseases, milk coming from the breast, hair growth, pelvic or lower abdominal pain, menstrual pain, and pain during sexual intercourse.
- Pregnancy histories (pregnancy, delivery, pregnancy outcomes and related complications).
- Sexual history (frequency of intercourse, sexual dysfunctions).
- Family history (whether there is an infertile member in the family, early menopause history in the family, birth defects, genetic disorders, mental retardation).
- Lifestyle (work, exercise, stress factors, weight changes, smoking and alcohol use).
What is investigated in physical examination and gynecological examination:
- Weight and body mass index (Increased body mass index is associated with decreased fertility, abdominal obesity is associated with insulin resistance).
- Development of secondary sex characters, body type (secondary sex character development is insufficient in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, short stature, mane neck is seen in Turner syndrome).
- Thyroid gland diseases (nodule in the thyroid gland, tenderness, size of the gland),milk discharge from the breasts, hair growth, pimples suggest an endocrine disorder, while it requires evaluation in terms of adrenal gland diseases, polycystic ovary syndrome, prolactin elevation, and hyper-hypothyroidism.
- Tenderness on gynaecologic examination is significant in terms of chronic pelvic pain and endometriosis.
- On gynaecologic exam structural anomalies of the vaginal and cervix, vaginal discharge, congenital anomalies of the uterus and tubes, infection and cervical factor are evaluated.
- On gynaecologic examination, the abnormal size of the uterus, irregularity of its structure, non-motility might be significant in terms of uterine anomalies, endometriosis and adhesions in the pelvis.
Evaluation of Ovulation:
- Menstrual pattern: (In women with ovulation, periods are regular, amount and duration of bleeding is fixed and they have premenstrual or menstrual complaints).
- Serum progesterone measurement: Serum progesterone levels reach their highest level 7-8 days after ovulation. Although 21st day of serum progesterone level > 3 ng/mL in a menstrual cycle lasting 28 days indicates ovulation it does not give information about the quality of the luteal period. Day 21 progesterone levels > 10 ng/mL in a normal menstrual period indicate a normal and healthy ovulation.
- LH test in urine: Ovulation can be followed at home with urine LH test kits and can give information about the time of ovulation. In general, starting on the 10th day of the menstrual period, the urine that is not too dense or too watery is checked in the evening. Ovulation is expected 24-48 hours after the color change is detected. However, home tests have 5-10% false positive and negative results.
- Follow-up of ovulation with serial ultrasonography: Although it is very reliable, it is costly and more laborious than other tests.
Evaluation of Fallopian Tubes:
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): While it gives information about the distribution of the contrast dye to the abdominal cavity after the passage of the contrast fluid through the tubes and exit from the tube ends, it also defines the congenital anomalies and pathologies of the uterine inner wall (polyps, myoma, uterine inner wall adhesions). HSG is done within 1-2 days after the end of menstrual bleeding. It is known that the sensitivity and specificity of HSG is approximately 65% and 84%. It does not give information about adhesions and endometriosis around the tube. It is necessary to repeat the uterine films older than 2 years. HSG might also have a therapeutic role. Tubes closed with mucus plugs can be opened with pressure while contrast material is administered during shooting.
- Chlamydia Ig G Antibodies: It is a painless, inexpensive, easy test that provides information about the presence of infectious damage in the tubes. In many studies it is shown that, Chlamydia infections cause infertility by damaging the tubes even without pelvic inflammatory disease history. In the world's leading infertility guidelines (RCOG guideline),it is recommended that all women be tested for chlamydia antibodies before HSG or any interventional procedure that will be performed to the uterus.
Evaluation of the Inner Walls of the Uterus:
- Hysterosonography: By giving physiological saline into the uterus, the diagnosis of polyps, uterine fibroids, adhesions in the inner wall of the uterus, congenital uterine disorders can be diagnosed by ultrasonography.
- HSG: In addition to the pathology in the tubes, it also evaluates the congenital or aquired structural anomalies of the uterus. Abnormal hysterosonography or HSG finding requires further examination such as hysteroscopy or laparoscopy.
- Laparoscopy: The role of laparoscopy in the evaluation of infertility is controversial. It is an expensive and invasive examination.
Laparoscopy can be performed in these situations:
- When endometriosis is suspected (painful menstruation, pelvic pain, deep pain in sexual intercourse),
- In the presence of pelvic adhesions and a history of disease in the tubes (pelvic pain history, complicated appendicitis, pelvic infection, pelvic surgery, previous ectopic pregnancy),
- In the presence of abnormal physical examination and HSG.
In patients with unexplained or male-induced infertility, laparoscopy is not required, as it does not change the treatment plan.
The tests that are not commonly used are:
- Poscoital Test: t should be done 2-12 hours after intercourse, just before the expected ovulation. It is not a routinely recommended test for investigating couples who present with a child request. It has no proven diagnostic value.
- Endometrial Biopsy: Provides information about whether ovulation occurs in the menstrual cycle and also luteal phase defects. It is done 2-3 days before the expected period. It is an expensive, invasive test that does not provide information about the inner wall of the uterus for embryo implantation, and is an unnecessary test for evaluating ovulation.
- Karyotype Analysis: Karyotype analysis is recommended for women diagnosed with early menopause (under 40),men with severe oligospermia, and couples with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
- Basal Body Temperature: It is a simple and inexpensive test used to evaluate ovulation by taking advantage of the heat-increasing effect of progesterone. Body temperature is measured and noted during the entire menstrual cycle without any activity in the morning. Basal temperature rise correlates with the LH curve, starting to rise two days before the LH surge. Although it is a guide for ovulation, it is a difficult test that can be affected by many factors and can vary according to the observer.
Initial Evaluation Of Man
Reproductive Story:
- Frequency and timing of sexual intercourse,
- Duration of infertility and a history of fertility in previous sexual partners,
- Childhood illnesses and developmental history,
- Systemic medical diseases (diabetes, upper respiratory system diseases),
- Past operations,
- Medication use and allergies,
- Exposure to gonadotoxins (environmental and chemical toxins and heat),
- Sexual history - including sexually transmitted diseases,
- General health: Diet, exercise, etc.
- Congenital anomalies.
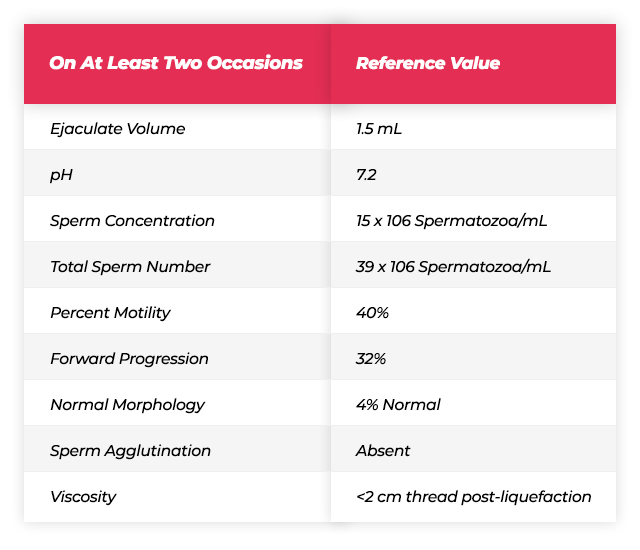
At Least One Sperm Analysis:
After 2-5 days of pre-test abstinence, the semen sample given to a sterile container by masturbation is examined within 1 hour. Normally, semen is liquefied in 20-30 minutes.
SEXUAL PERIOD SHORT; Volume and concentration decrease, motility and morphology do not change.
IF SEXUAL PERIOD IS LONG; As volume and concentration increase, motility and morphology do not change, dead sperm increases.
Ideally, two sperm samples should be evaluated at least 1 month apart.